|
-
Tides occur because of the pull of gravity of the Moon and the Sun on the Earth's oceans. Because the Moon is
closer to the Earth, it has the greatest effect on our tides. There are approximately 2 high tides and 2 low tides every 24
hours.
-
Spring tides (often called 'king tides' by fishermen) occur at New Moon and Full
Moon when the Sun, the Moon and the Earth are in line. This forms extremely high high-tides and extremely low low-tides.
-
Neap tides occur at First Quarter and Last Quarter, when the Sun, the Earth
and the Moon are at right angles. This forms quite low high-tides and quite high low-tides.
Tides are periodic rises and falls of large bodies of water. Tides are caused by the gravitational
interaction between the Earth and the Moon. The gravitational attraction of the moon causes the oceans to bulge out in the
direction of the moon. Another bulge occurs on the opposite side, since the Earth is also being pulled toward the moon (and
away from the water on the far side). Since the earth is rotating while this is happening, two tides occur each day.
Isaac Newton (1642 -1727) was the first person to explain tides scientifically. His explanation of the tides (and many other phenomena)
was published in 1686, in the second volume of the Principia.
The Sun's Interaction with the Tides
Spring
Tides
 Spring tides are especially strong tides (they do not have anything to do with the season Spring). They occur when the Earth,
the Sun, and the Moon are in a line. The gravitational forces of the Moon and the Sun both contribute to the tides. Spring tides
occur during the full moon and the new moon. Spring tides are especially strong tides (they do not have anything to do with the season Spring). They occur when the Earth,
the Sun, and the Moon are in a line. The gravitational forces of the Moon and the Sun both contribute to the tides. Spring tides
occur during the full moon and the new moon.
The eccentricity of the orbit of the moon in this illustration is greatly exaggerated. |
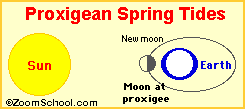
The Proxigean Spring Tide is a rare, unusually high tide. This very high tide occurs when the moon is
both unusually close to the Earth (at its closest perigee, called the proxigee) and in the New Moon phase (when the Moon is between the Sun and the Earth). The proxigean spring tide occurs at most once every 1.5 years.
Neap Tides
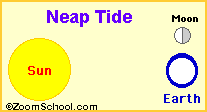 Neap tides are especially weak tides. They occur when the gravitational forces of the Moon and the Sun are perpendicular to
one another (with respect to the Earth). Neap tides occur during quarter moons. Neap tides are especially weak tides. They occur when the gravitational forces of the Moon and the Sun are perpendicular to
one another (with respect to the Earth). Neap tides occur during quarter moons.
|

